At present, over 10,000 FinTech startups are operating around the world. The theme which is right on the top of the FinTech industry in terms of capital saturation and entrepreneurial activity is lending and payments. Such innovations triggered financial markets to change from ‘winners take all’ attitude to the productive stage of exploration and collaborative relationships. In this context, I would like to bring in two different perspectives via which payment models are evolving.
From an Infrastructure standpoint, central banks of few countries are coming with robust set up to connect commercial banks. Although it is an old phenomenon yet, it improved drastically in the past few years. One of the leading systems in it is from China’s Internet Banking Payment System (IBPS) with current operating SLA of successful interbank payments with acknowledgement is 20 Sec. Processing credit transfers as push payments and direct debit as pull payment, this ISO20002 certified solution operates on China National Advanced Payment System (CNAPS-II). By 2018, IBPS handled approximately 6Billion payments to the tune of 50 Trillion Yuan. Similarly, NPCI UPI model of India is showing great potential and an estimate from RBI, by 2021 digital payments in India will grow by four times. Major characteristics of this system are to have robust back end availability for entities to come up with various front-end solutions. As an example, India’s UPI system build on single payment API and few supporting API.
The other bit radical solution is the bank-owned front end. Example – Zelle in US and MoneyTap is Japan. Cryptocurrency frameworks trigger these solutions and established by Ripple’s blockchain technology. Ripple is a San Francisco based company which conceptualized the blockchain payment system and popularized it as Ripple Payments. To visualize this, consider all banks use an app of your mobile phone for payments. Ripple is rapidly expanding and at present, looking at the possible option for currency exchange and foreign payments. As using Ripple’s blockchain banks are enabled to reduce competitive transaction fees as well as currency conversion fees. Japan and US banks have pioneered Ripple payments, and various Asian and European banks are coming up with their versions.
Both models mentioned above are the future of payments and have their advantages and disadvantages. These innovations are also raising questions about the future of existing scheme payments networks (like Visa, Mastercard, Amex) What would be the role of tech companies in future? Are banks losing control over the payment’s ecosystem? How will be the future payment business model? As the predominant carriers listed here are api based and blockchain-based payment systems, so it is worth having some technical insights, defining these disruptive technology paradigms.
Ripple vs SWIFT:
Ripple payments are getting significant traction on International payments ecosystem which is ruled by SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) since 1973. At present, 11000-12000 banks and other financial institutions take advantage of SWIFT for International payments. SWIFT’s reach is across all continents and almost all countries. Messages on SWIFT are growing every day and processing close to 35 million FIN messages per day.
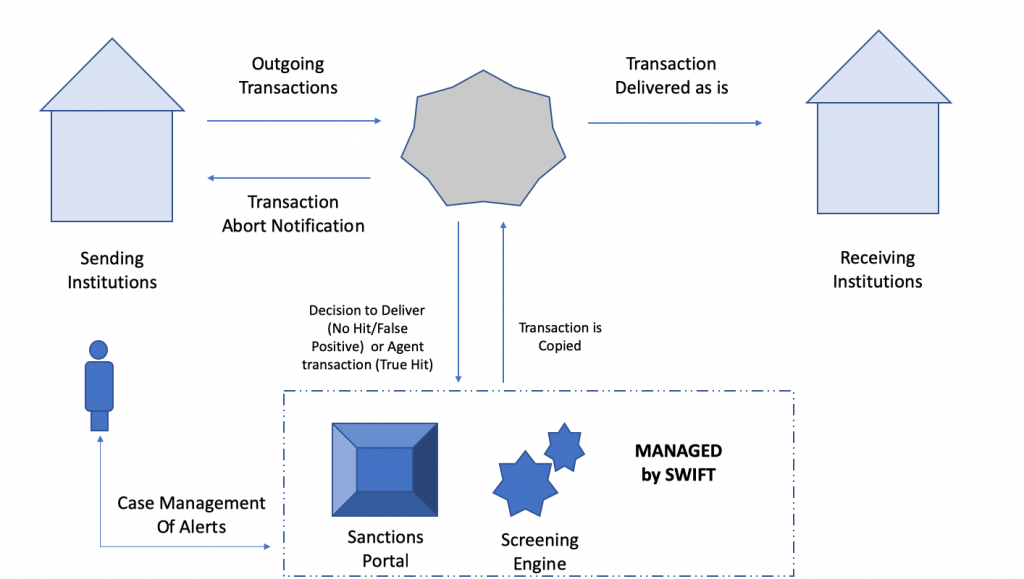
SWIFT transaction flow:
SWIFT is a massaging network connected through various banks. Once a bank registered through SWIFT, they receive a SWIFT code which is known as a bank identification number (BIC), SWIFT cost, SWIFT ID or ISO 9362 code. SWIFT is a messaging network to transfer information among banks. It does not have any capacity to hold money or securities. SWIFT payments flow takes hours to days for completion of the single payment. Data flow is also through a secured network and sometimes, difficult to track by originator bank in case of any issues.
Ripple Transaction Flow – Deep dive:
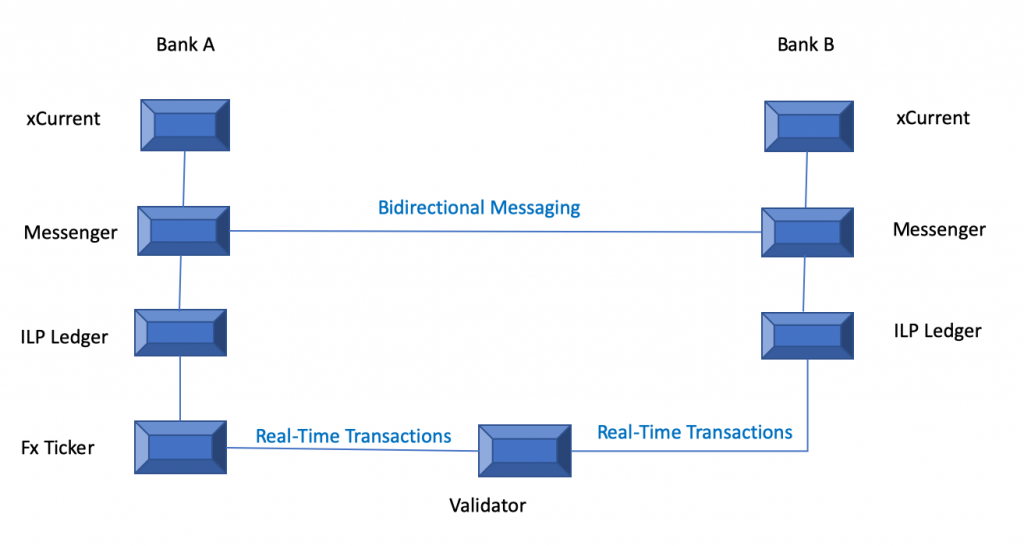
Instead of ‘to and fro’ messaging system of SWIFT for payment processing, Ripple uses xRapid and xCurrent solution. xRapid designed for the cross-border remittance whereas xCurrent focuses on settling and tracking of the cross-border payments. xCurrent system constitutes four primary parts:
1. Messenger: For bidirectional communication between RippleNet banks, the messenger of the beneficiary bank connects with the target bank’s messenger to share information such as KYC, fees, foreign exchange rates, payment details, delivery timestamp and fees related information. Thus, the total cost of the transaction is known to the beneficiary bank upfront.
2. FX Ticker: This xCurrent component helps in the settlement of foreign exchange rates. Every bank has its FX tracker and connects with other RippleNet’s FX tracker to share information about Foreign Exchange rates in real-time. It also governs currencies, accounts and authentication credentials for network’s ILP ledgers. During the payment process, it validates Foreign Exchange quotes before transferring the details to ILP ledger of the destination bank.
3. Validator: It generates an encrypted confirmation of whether the payment is successful or failed. It sits in the middle of the communication between sender and receiver and makes sure that their respective ledgers and debited and credited. It is the single source of truth between sender and receiver for the particular payment transaction.
4. ILP Ledger: As a financial ledger system, ILP ledger keeps track of all credits, debits and liquidity across the banks involved in the payment transaction. With the help of ILP ledger, all payments settle instantaneously irrespective of the number of parties involved or volume of the transaction. Hence, it helps banks to have low cost, high profitable and instant international payment capabilities.
SWIFT gpi:
To counter the growing popularity of Ripple payment, SWIFT came up with SWIFT gpi in 2017. They intend to reduce the lead time of International Payment from the traditional SWIFT process. It was designed to use the existing SWIFT network and collaborating with the banks. With SWIFT gpi design as a cloud-based mechanism where payment issuer can track the status of the initiated payment transaction at each processing level. Approximately 150 banks have already adopted SWIFT gpi and were able to process International payments within a day.
Interestingly, SWIFT also understands the potential of Blockchain technology and the growing threat of his competition with Ripple payments. Though on records officials of Ripple stated that Blockchain is not yet matured enough to handle sensitive International payment, yet they are putting a lot of efforts in Research and Development for the same. Already, one Belgium based Organization has launched a Proof of Concept gateway, named as gpi Link with Enterprise Blockchain solution provider R3 to integrate with its existing network of gpi payment. A lot of traction in this sector makes the ground for many disruptive solutions to explore.
| FinTech | With solutions such as UPI and Ripple, FinTech’s are winning share from banks and scaling at rapid speed. |
| Schemes (Visa/Mastercard) | Domestic association and alternate solutions are breaking down their profit-driven franchise model |
| Merchant | Innovative ways to accept and streamline payment:
– PoS and non-PoS cardless payments – App to App payments – Social commerce |
| Customer Behavior | Faster adoption of new payment methods and higher expectation towards new services |
UPI:
On one hand, Ripple is gaining its market share against traditional SWIFT network, on the contrary, UPI payments have already taken a lead in terms of traditional scheme based online payments. This lead is both in terms of traction as well as transaction volumes, especially in the Indian context. Reason for their success is the UPI payment model. Unlike creating UPI as a product, it is developed as a platform. With a robust infrastructure is in place, UPI made sure that domestic payments process remains secure and straight forward. Once it is created, due to its ease of use and open platform, many banks and financial institutions have quickly developed their own front-end and mobile applications and invested heavily in marketing to gain their customer’s attention. Many start-up and FinTech companies also joined the league to gain their share of the pie. Another advantage of UPI architecture is, it allows inter-operable payments. Any user of UPI can transfer money to any UPI user irrespective of application it is using which means it allows payments between any bank user to any FinTech application user seamlessly.
UPI: Technical Landscape:
The main differentiator of Unified Payments Interface or UPI is sender and receiver identities are hidden behind a virtual identification. The verification of sender and receiver is called a two-factor authentication process which is more secure than traditional card-based payment methods. This also removes a banking institution to take up the authentication process for other bank’s customers. Another challenge of traditional payment system is the validation of recipient demographic details which stored in a different format in banking and financial institutions and very sensitive as well. UPI simplified it by adding two types of payment IDs which are global identifiers and Virtual payment address (VPA). The global identifier is driven via mobile or Aadhar number of the sender/receiver and VPA is an identifier issued by the bank such as abc@bank. Any user can have multiple VPA as per their choice. Once the sender and receiver authentication are done, the UPI system uses any existing payment rail to process the transaction. Since in this model, sender and receiver trust is not required so the entire payment process becomes smooth.
UPI payments already made a dent in credit card business and took a big share of wallet business in 2018-19.
Impact of disruptive payment models in the payment ecosystem:
| FinTech | With solutions such as UPI and Ripple, FinTech’s are winning share from banks and scaling at rapid speed. |
| Schemes (Visa/Mastercard) | Domestic association and alternate solutions are breaking down their profit-driven franchise model |
| Merchant | Innovative ways to accept and streamline payment:
– PoS and non-PoS Cardless payments – App to App payments – Social commerce |
| Customer Behavior | Faster adoption of new payment methods and higher expectation towards new services |
Critical success factors for the banking and financial institutions:
• Since various FinTechs are coming up with innovative ideas and receiving significant funding, banks need to explore opportunities of investment and partnerships with such Fintechs and made their culture adjusted to the new ecosystem.
• With the inclusion of Blockchain and api based payments, it is clear that these technologies are the future. Hence, banks need to be ready with their infrastructure to quickly adapt the same and find out solutions of their inherited complex software setup.
• Rate of disruption in the payment ecosystem is faster than ever before. Hence, banks need to be agile in decision making and adaptability.
• End-user of banking chain is coming closer to act as a direct customer for the banks, so reassessment of the entire value chain is critical for the success in the long run for banking and financial institutions.
• Payment process creates and consumes the humongous amount of data which can be used for various possible ways. Bank’s need to rethink how it can be utilized to generate revenue and customer preposition before any third party does it with their data.
The new proposed disruptive banking model:
Disruptive technologies have blurred the boundaries of the digital financial world. On the one hand, api based payment solutions taking the business away from banks, whereas blockchain-based method can help to get the control back to banks. However, consuming these technologies require many efforts at the core infrastructure level of the banks. Traditional banking systems are still managing the burden of vertically integrated core banking infrastructure. Whereas, an api approach requires horizontal integration. Digital disruption pushing the boundaries of all businesses, including banking and financial sector. With the success of Facebook, Amazon, Uber and Google over the years, it is clear that industry is heading towards platform-based strategy and leaving the traditional product-based standalone approach.
The banking sector also needs a similar impetuous to move towards a platform-based model. Heart of this model is open api and disruptive technologies to provide an open field for aggregators and FinTech to flourish. Digital ecosystem grew due to its capability to scale rapidly and providing opportunities to innovation and aggregation. Banking systems and infrastructure can avail this opportunity to emphasize on horizontal integration, which is only possible by enabling external third parties to innovate on their open infrastructure as UPI did. Hence, having such models in place is not an IT but a business strategy for the banking sector to adopt, which constitutes:
• Converting their infrastructure to API marketplace with a focus to improve the security and sensitivity of customer-centric data
• Enhance user experience to become your customer’s favourite bank rather than the only bank
• Focus on becoming a trustworthy financial advisor to give a holistic view of customer’s financial needs and seamless user experience
• Become partners with FinTechs by creating incubation centres to enable innovation and integration without impacting daily operations
• Collaborate with industries and become strategic partners of their technological innovations
• Move towards banking as a service model for FinTechs and aggregators to take first-mover advantage of disruptive technologies
• Follow 20-60-20 business model which involves efforts on 20% innovation, 60% maintenance and most importantly, 20% reduction of the systems periodically.
World Economic Forum (WEF) already predicted the future of banking and the FinTech ecosystem. Accordingly, they created a consortium of banking and financial services to focus on many areas, which includes the most critical cybersecurity aspect in the payment industry. Any technological disruption comes with immense opportunities and the onus is with the banking sector, how well they can utilize it. Right now, disruption is visible in the payment sector and soon it will spread and took over other traditional financial sectors. In such a scenario, it will be interesting to see how the future will be shaped up with the technological advancements and their impact on banking and financial sector’s strategic approach.
#payments #Banking #Payments #pgpx #iima






Recent Comments